B
Professor(教授) Jemima Gryaznov answers some questions about memory (记忆).
Q1: Why can I remember things in my childhood but not what happened last week?
A1: We remember things that have strong relations (关联) in our mind, especially emotional (情绪的) ones. Childhood memories are often these, because when we experience things for the first time, we often have strong feelings of fear (害怕) or excitement. Also, interesting or funny childhood stories are often told again and again. As a result, we remember them much better, as retelling (复述) events helps fix experiences in our memories. So when remembering something new, find its relation to our emotions, or retell it to others.
Q2: Do some people really have a photographic memory (过目不忘的记忆)?
A2: A person with a photographic memory could remember everything of a picture, a book or an event many years later, but no one knows if there is this kind of person. However, some people do have amazing memories. For example, Daniel Tammet can remember the first 22 514 digits (数位) of $pi$ and Stephen Wiltshire can draw a detailed picture of a city from memory after flying over it in a plane. They are both good at remembering things. As most of us do not have amazing memories like them, a good way to remember things is to group similar ideas or information together.
Q3: Why do I forget the new words that I learnt yesterday?
A3: Don’t worry. This is natural for many people. In 1885, Hermann Ebbinghaus showed us a famous forgetting curve (遗忘曲线). According to him, the quickest loss (丢失) of memory happens during the very early time after learning, and then it gradually (逐渐地) slows down. This means that going through (复习) what we have learned in time can help us to remember the information better.
(
B
) 4. According to the text, a person with photographic memory ______.
A. has strong feelings of excitement B. remembers details clearly years later
C. forgets what he has learned quickly D. likes retelling stories to others
(
B
) 5. Which two words are the best for the mind map of Q1 and A1?
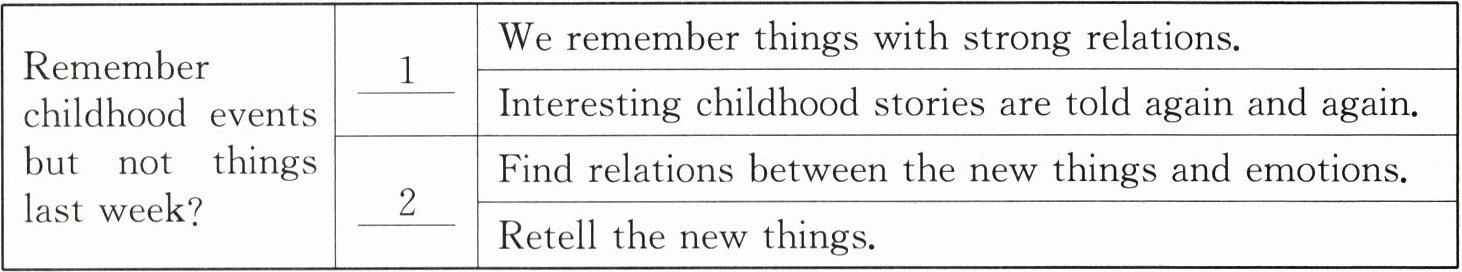
A. 1: Reasons; 2: Results
B. 1: Reasons; 2: Advice
C. 1: Advice; 2: Results
D. 1: Results; 2: Advice
(
D
) 6. To remember things better, ______ is NOT talked about in the passage.
A. grouping similar information together
B. finding relations between things and emotions
C. going through what we have learned
D. drawing a picture of the things we have learned
(
A
) 7. ______ best shows the forgetting curve.
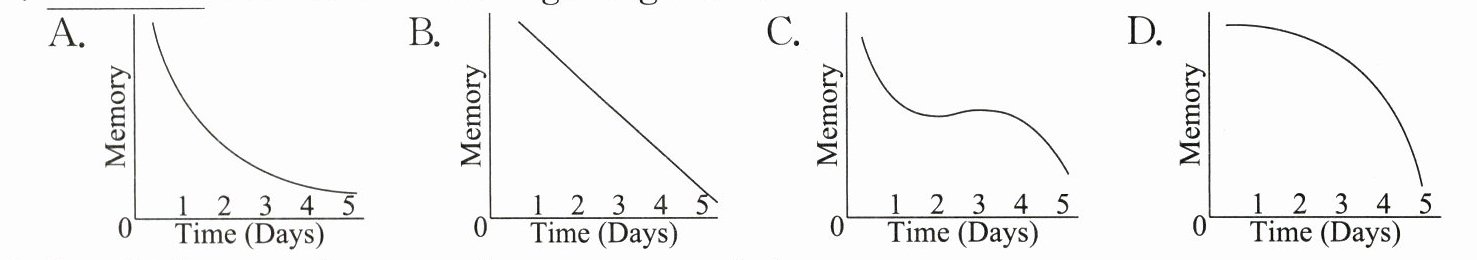
(
B
) 8. In which part of a magazine can we read the text?
A. Travelling. B. Learning. C. Health. D. Nature.